Tingling in hands? Pains in hands?
What is the reason for tingling in hands?
There are many different reasons for tingling and pains in hands, therefore, first, a careful examination is required. The most common reason of numbness sensation is the compression neuropathy or nerve entrapment. There are more than 20 types of compression neuropathy. Carpal and cubital tunnel syndrome is two most common diseases in this group of diseases.
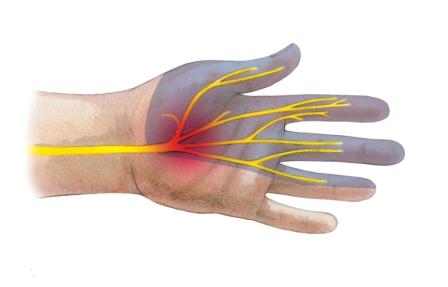
Compression neuropathy expresses the essence of the disease – a nerve is compressed. Usually, the nerve is being compressed in the narrowest points, therefore it is also referred to as the tunnel disease. The nerve is being compressed in the carpal tunnel – in the wrist or in the cubital tunnel – in the narrow passageway in the elbow area. The carpal tunnel syndrome is much more frequent than the cubital tunnel syndrome.
What is the carpal tunnel syndrome?
The nerve compression most often tends to develop in the wrist – in the carpal tunnel. This is a passageway between the wrist bones and wrist ligament through which the extensor tendons and median nerve run, which controls sensitivity of fingers.
What causes the carpal tunnel syndrome?
The nerve entrapment can be caused by overload, protracted, monotonous movements, various diseases, as well as traumas. As a result of protracted pressure part of the nerve fibres fades entailing the movement and skin sensitivity disorders.
Symptoms
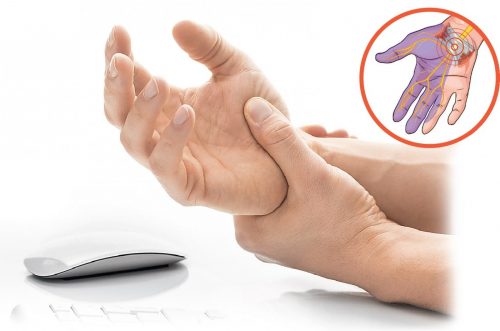
The first symptoms are tingling in fingers, burning sensation and pains, oftener in the dominant hand. If the person is right-handed, then the nerve entrapment develops in the right hand, since the load is greater exactly on this hand, for the left-handed – vice versa.
Reasons
The carpal tunnel syndrome oftener develops in those, who do monotonous manual work, overload the hands and fingers, doing one and the same movements, work with arms raised or keep hands in a tight position. Historically the carpal tunnel syndrome used to be called a milkmaid disease, because it most often tended to develop in women, who throughout their life were milking cows with hand. Nowadays work becomes easier, heavy manual work is being replaced with new technologies, computers and modern equipment, however, the spread of this disease does not decline. The disease is not always connected with heavy and /or monotonous work, it can develop in people, who do not do anything heavy every day. The carpal tunnel syndrome is spread in women four times more than in men. This condition oftener tends to develop in people who suffer metabolic and hormonal disorders, diabetic patients, people with impaired thyroid functions, rheumatoid arthritis.
The most common disease manifestations:
- Progressive numbness and pains in hands, specifically at nights,
- Swelling, numbness in fingers from morning,
- Movement disorders in wrists, weakness of hands,
- Disability to grasp and hold tiny items.
For information: The nerve entrapment left untreated for a long time drastically impairs the quality of life – the fingers sensitivity disorders become more and more pronounced, eventually the wrist muscles weaken and the wrist loses strength, entailing disability to perform simple daily work.
If left untreated on time, the pains and tingling tend to spread all over the hand involving disorders in the wrist functions.
Diagnostics
To identify the tingling reason and start appropriate treatment you need to visit a neurologist or neurosurgeon. To choose the most appropriate treatment method to mitigate pressure on the nerve and facilitate regeneration of the damaged fibre, first, it is necessary to ascertain the place and degree of the nerve damage. Diagnostics is significant, because treatment, which differs in each case, depends on diagnostics.
- Neurosurgeon’s consultation. If complaints become permanent and do not disappear within 2–3 weeks, you need to seek medical advice. It is important to find out the reason for the complaint, if necessary, to assign relevant examinations to take a decision on the most suitable treatment tactics
- Neurography. Measures the velocities of motor and sensory nerve impulses to identify the nerve fibre damage, its character and degree.
- Ultrasound. Provides additional information on changes in tissues adjacent to the nerve – in tendons, joints and bones.
Additional diagnostic opportunities
If there are suspicions that the hand tingling and pains are caused by other disease to specify diagnosis it is possible to use X-ray, electromyography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, lab tests etc.
- Computed tomography scan enables to see well the bone growths, cartilage, horns, thickened ligaments.
- Electromyography helps detect the nerve viability and conductivity.
- Blood test is performed to detect whether there is inflammation in the organism.
- Ultrasound is performed if around the nerve there is something suspicious, for instance, enlarged joint capsule or there is another uncertain formation.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is performed if there is a suspicion that the nerve is entrapped somewhere else, for instance, in the cervical spine. Magnetic resonance imaging shows the nerve structure, spinal cord, spinal cord roots.
Treatment opportunities?
The main target of treatment is to mitigate /eliminate the nerve entrapment. There are various methods and auxiliary aids to help temporarily eliminate unpleasant sensation and relieve the current condition.
Depending on the nerve damage degree there are various opportunities.
- Sparing regimen. In case of mild compression neuropathy, where symptoms have just appeared, it is recommended to spare the hand more.
- Pharmaceutical therapy. In mild cases pharmaceutical therapy is used involving local injections. Such treatment includes using anti-inflammatory agents, steroid injections or blockades as well.
- Physical therapy. Ultrasound using liniment, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis and other procedures helps mitigate oedema and relieve the nerve entrapped. Also using special orthosis that enables to hold the hand in the right position helps well.
- Surgery. To relieve the nerve entrapment either the conventional method or the cutting – edge and much less traumatic endoscopic method is used.
- Conventional surgical operation is performed under local anaesthesia. A small cut into the skin is made on the heel of the palm (or the inside surface of the elbow), the passageway is opened and the nerve is relieved from compression. After surgery it is necessary to follow a sparing regimen for one month.
- The endoscopic method, if compared to the hitherto used surgical treatment method, is much more sparing to the patient. This is a new, revolutionary method of treatment of tingling in hands – nowadays Gold Standard in the world and in Latvia. This method is specifically suitable to high – risk patients with difficulties in wound healing (diabetes mellitus, peripheral artery, metabolic etc. diseases). During the operation a miniature endoscope – a video camera and microscopic surgical tools are administered through a small cut in the skin into the carpal (or cubital) tunnel to help relieve the compressed nerve.
The endoscopic method, if compared to the hitherto used surgical treatment method, exhibits a number of advantages:
- minimal cosmetic defect
- shorter and less painful post-surgical period
- early restoration of ability to work
Surgery delivers results in long term – a possibility to work and sleep in comfort again.
The surgery is performed under local anaesthesia at Medical Clinic “Medicīnas centrs ARS” Day Patient Department. The patient already on the same day immediately after surgery can go home.
At Medical Clinic “Medicīnas centrs ARS” Day Patient Department you can undergo:
- Minimally invasive (endoscopic) surgical treatment of stenosing neuropathy (carpal, cubital, tarsal etc, tunnels)
Treatment of the carpal and cubital tunnel syndrome is performed by
- Neurosurgeon – vertebrologist DM Janis SLEZINS
- Neurosurgeon – vertebrologist DM Raimonds MIKIJANSKIS
VIDEO:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome (LV)
- Carpal tunnel diagnostics and treatment. (LV)
- Carpal tunnel surgery (LV)
PUBLICATION:
- Tingling in hands … (LV)