Dr. Solveiga Zālīte, ophthalmologist, neuro-ophthalmologist of the “Medicīnas centrs ARS”, introduces the new facility.
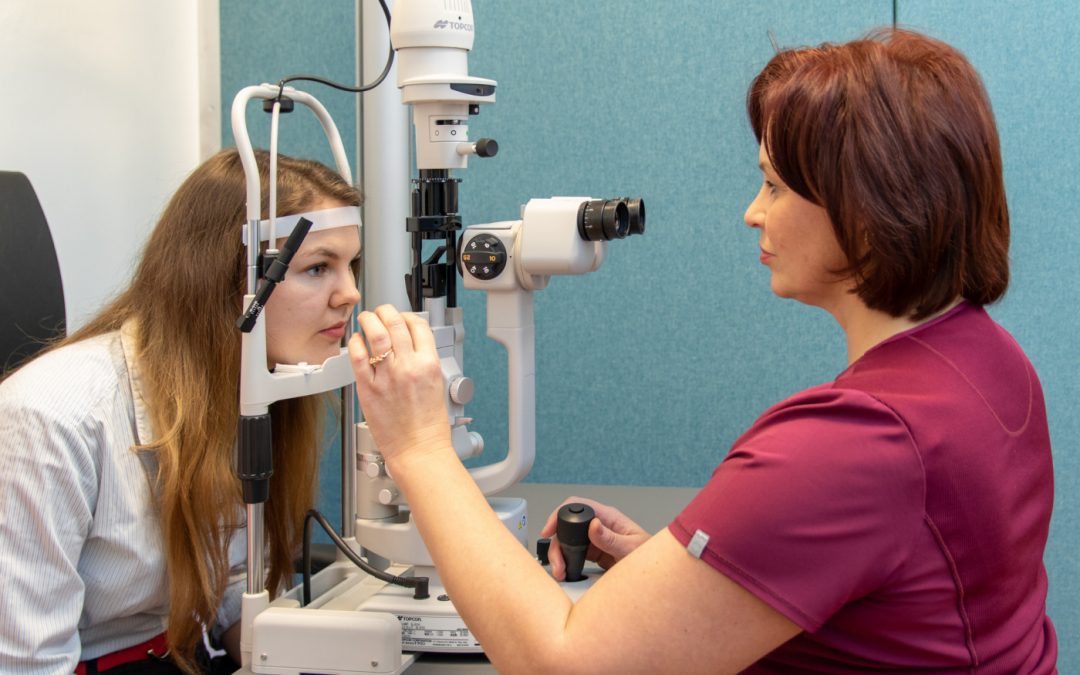
A new modern ophthalmology (eye disease) facility specialising in the detection, treatment and prevention of visual impairment and eye diseases has been opened at the ARS Medical Centre.
The new facility will provide services delivered by a staff of highly qualified ophthalmologists and optometrists who will perform eye exams using state-of-the-art devices and modern examination techniques to assess visual functions, identify the causes of eye diseases and prescribe appropriate therapies, if necessary. They will also select appropriate means for optical vision correction and recommend the best ways for prevention.
Diagnostic devices and methods
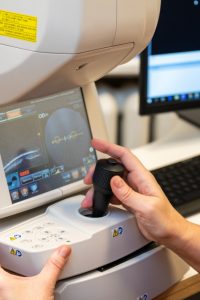
Autorefractor keratometer: a computerised system used to examine the refractive ability of the optical system of the eye to detect refractive disorders of the eye (myopia or near-sightedness, hyperopia or far-sightedness and astigmatism).
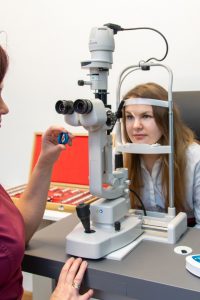
Digital foropter: a device used to examine visual functions, determine visual acuity, select eyeglasses according to the dioptre strength, detect functions of binocular vision, examine double vision (diplopia), check colour vision and test contrast sensitivity.
Tonometers: tonometers of the latest generation are built into autorefractor keratometers and are combined with a pachymeter, a device used to measure the thickness of the eye cornea, which is important in assessing intra-ocular pressure (IOP) values. Use of several devices combined into a single device provides immediate information on intra-ocular pressure.
Contactless tonometry is used as a screening method. Where a patient has elevated intra-ocular pressure according to contactless tonometry measurements, the pressure measurements should be done using contact tonometry techniques, e.g. iCare tonometry.
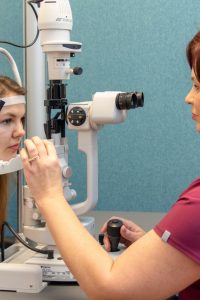
Biomicroscopy: an exam in which a special lens is placed before the eye to examine and evaluate the front and back of the eye. Eye drops are used before the exam for a complete examination of the retina. Sometimes fluorescein in the form of orange droplets is used to diagnose corneal damage; the white part of the eye (sclera) may turn yellowish for a short time.
Computer perimetrytest(visual field test) is used to determine the visual fields (central and peripheral) of the eye. This exam plays an important role in diagnosticating glaucoma and assessing its progression as well as in evaluating the efficacy of treatment. It helps diagnose neurological pathologies and is also used in case of retinal disorders. The visual field test is also performed on drivers of motorised vehicles.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT)test is a method of structural examination of the optic nerve, retina and cornea of the eye. It enables taking photos of the back of the eye, analysing eye structures in cross-section, analysing the features of the surface of the retina, the structure of the retina, the thickness of the retinal nerve fibre layer. It is used in diagnosticating glaucoma and retinal disorders (age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic macular oedema etc.), monitoring disease progression and in evaluating therapy.
Dioptrimetry helps determine the dioptre settings of eyeglass lenses. Analysis of monofocal (spherical and cylindrical), bifocal and progressive eyeglass lenses is possible. Using the data obtained, an ophthalmologist or optometrist assesses whether the eyeglasses used currently are appropriate and prescribes new ones if necessary.